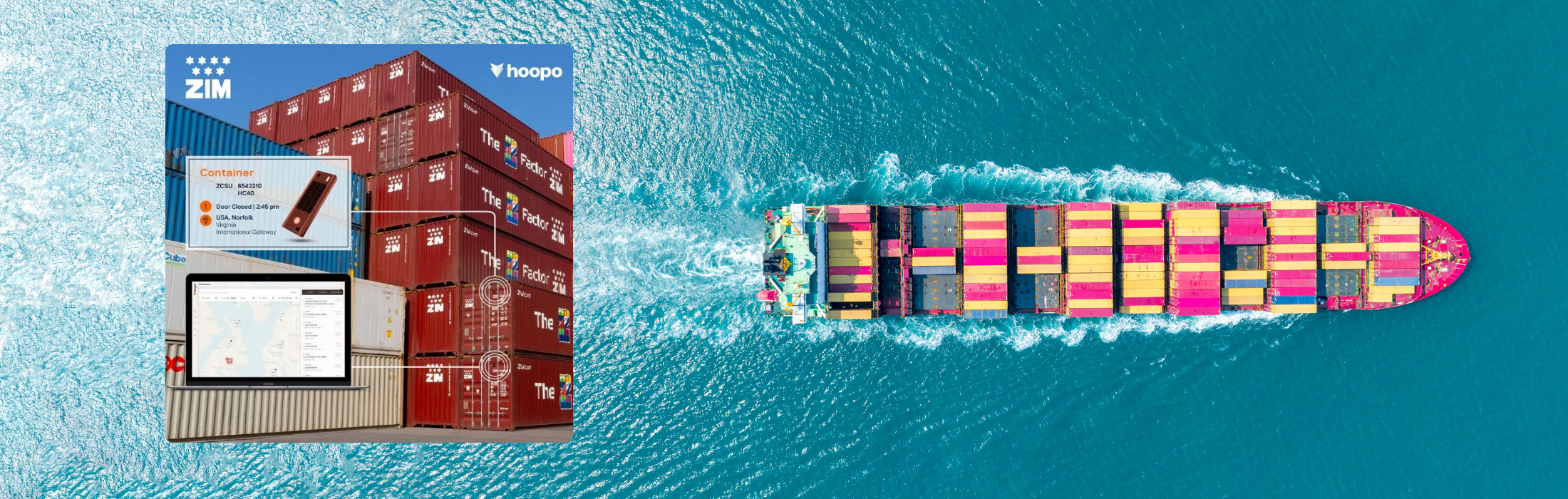
Israel Standardization Policy
The Ministry of Economy’s Standardization Administration is in charge of implementing the national standardization policy.
Why Standardization is Important?
Improving product quality
Ensuring product safety
Increasing the Israeli industry’s ability to compete in domestic and international markets
Removing international trade barriers
Facilitating mutual acceptance of products between Israel and allies, by inspecting products’ compliance to standards
Standardization as Basis for Economic Growth
- Access to markets: facilitating trade by preventing international trade limitations, opening new markets and expanding existing ones
- Product safety: limiting the risk to the consumer, as well as the financial risk to the entrepreneur, by relying on standardization and regulation
- Risk management: a means of assessing risks and taking precise action to minimize their effect, at a reasonable price
- Cost reduction: optimizing the product plan throughout its life – planning, manufacturing, marketing, recycling
- Innovation: operational compatibility as well as measurement and performance-comparison abilities facilitate product introduction and market penetration
- Environmental Protection: minimizing negative environmental effects and improving sustainability by recycling planning
- Energy efficiency: the ability to measure energy efficiency enables educated use and prioritizing energy-saving products and processes
- Quality management: improving quality, reliability and consumer satisfaction
- Supplier-client relationship: determining a clear and measurable basis for the commitment between seller and buyer
- Social responsibility: management ethics, corporate responsibility and norms of behavior
Implementing the National Standardization Policy
Adopting International Standards
Another amendment to the Standards Law was confirmed by the Knesset in late 1999, and determined that when setting a standards the SII should, as a rule, adopt international standardization that is widely accepted in developed countries. In setting such a standard, the nature of trade between Israel and other countries will be taken into consideration. When various different standards exist in developed countries, the SII may determine an alternative standards, provided that any standard so determined will be fully based on an existing one.
In special circumstances, when strictly necessary due to conditions unique to the State of Israel, the SII may change certain conditions stipulated in international standardization, while detailing the reasons in the explanation attached to the standard.
Lowering Cost of Living:
- Removing import restrictions: adopting international standards and accrediting foreign laboratories, while cancelling import duties and double fees.
- Minimizing the variety of products that require SII authorization, thus significantly lowering costs for local manufacturers, who will be able to import raw materials more easily.
- Enhancing supervision processes over market products
- Cooperation with the SII to determine areas of possible concessions for local manufacturers – improving service, lowering prices and minimizing interference with business activity.
The Regulator’s Role on Standardization
The Government takes an active role in ensuring product safety by involvement in setting standards, inspecting product compliance and enforcement in the marketing stage.
More related articles...


Introduction to the Israeli Import Reform
The Import Reform The import reform focuses on changing the methods of regulating imports into Israel, moving to declaration-based tracks instead of inspections, for a


Challenges and opportunities in trade
Tambien disponible en español | Egalement disponible en français The tensions we are now seeing in the international trading system have been building over decades. Many people


The Importer’s Practical Guide
The process of importing to Israel includes a series of measures, which you, as an importer, should be familiar with before executing an import transaction.


Customs Release Process- All The Essential Documentation For Importers
Any imported commercial product arriving in Israel is required to complete a customs release process. We recommend that you consult a suitable professional in order


An EU approach to enhance economic security
The European Commission and the High Representative today published a Joint Communication on a European Economic Security Strategy. This Joint Communication focuses on minimising risks


Wartime macroeconomics
A fresh supply shock stemming from the war in Ukraine will deal a blow to the economic recovery from COVID-19. The energy and food sectors