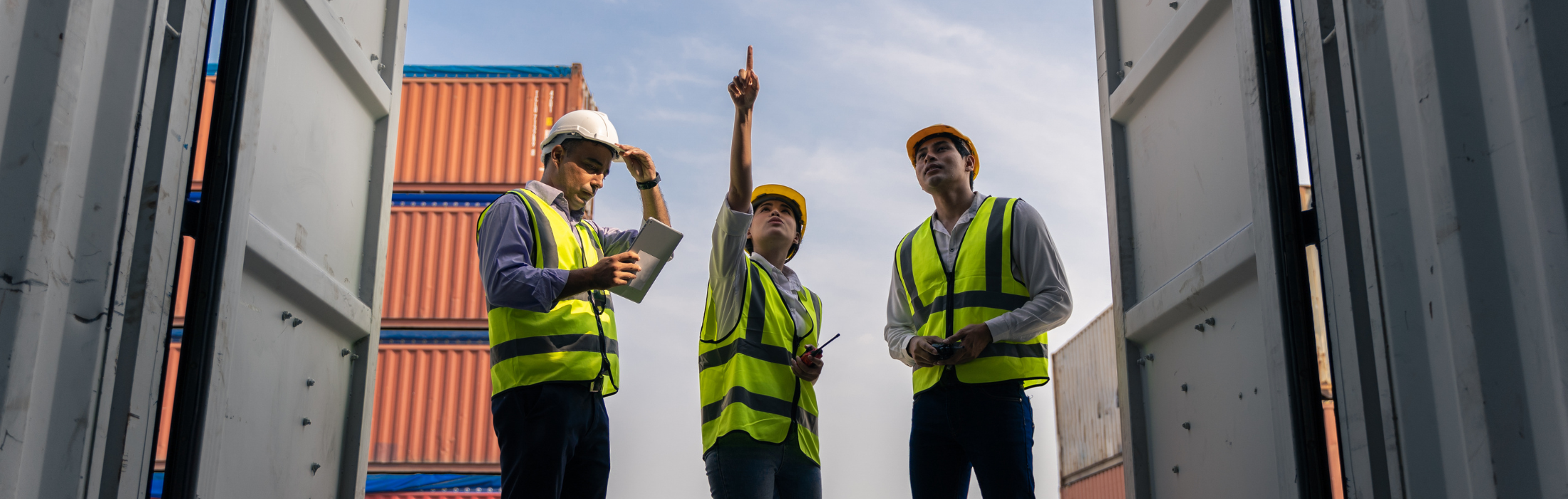
1. What is customs brokerage, and why is it necessary?
Customs brokerage is a professional service that helps importers and exporters clear their goods through customs efficiently. Brokers handle document submission, tax calculation, compliance with regulations, and potential delays, ensuring a smooth import process.
2. What are the main responsibilities of a customs broker?
A customs broker:
- Reviews and corrects import documents (invoice, packing list, etc.).
- Calculates taxes, duties, and fees.
- Submits customs declarations correctly.
- Handles disputes and delays with customs authorities.
- Advises importers on regulatory compliance.
3. Does every importer need a customs broker?
Not always. Private individuals or small businesses handling minor shipments can sometimes clear goods themselves. However, for commercial imports or regulated products (electronics, food, pharmaceuticals), a customs broker is highly recom
4. How much does a customs brokerage service cost?
The cost varies based on the type of goods, shipment value, origin, and complexity. It may include:
- A fixed brokerage fee or a percentage of the shipment value.
- Customs clearance fees.
- Additional surcharges like port storage.
It’s best to request a quote before importing.
5. What documents are required for customs clearance?
To clear goods through customs, you need:
- Commercial Invoice
- Bill of Lading / Airway Bill
- Packing List
- Regulatory approvals (if required, e.g., for food or cosmetics)
6. How are import taxes calculated?
Import duties and taxes depend on:
- The declared value of the goods.
- The applicable customs tariff for the product category.
- VAT, purchase tax, or additional charges if applicable.
7. What happens if there’s an error in the customs documents?
Errors can lead to delays, fines, or goods being held at the port. A customs broker quickly corrects and resubmits the documents to minimize disruption.
8. Can I clear goods without a customs broker?
Yes, but it’s complex for commercial shipments. A customs broker simplifies the process and prevents costly mistakes, especially for regulated goods.
9. What types of inspections does customs conduct on shipments?
Customs inspections include:
- Document review – Ensuring the declaration matches the goods.
- Physical inspection – Checking if the shipment matches its description.
- Regulatory inspection – For sensitive products (medications, food, etc.).
10. What causes customs delays, and how can they be avoided?
Delays may result from:
- Errors in documents.
- Additional inspection requirements.
- Discrepancies between the declaration and shipment.
- Unpaid duties or fees.
Using a customs broker and ensuring correct paperwork can prevent delays.
11. How can I check if a product requires special approval before import?
Check the official customs and government agency websites (e.g., Ministry of Health, Standards Institute). A customs broker can also verify regulatory requirements.
12. What does “release under payment condition” mean?
This means customs releases the goods only after all taxes and fees are paid. Failure to pay on time may result in storage fees or delays.
13. Can I dispute a customs decision?
Yes, if you believe customs applied incorrect duties or regulations, you can file an appeal. A customs broker can help submit a formal request.
14. What is an Original Bill of Lading, and when is it required?
An Original Bill of Lading proves ownership of the goods. It’s often required for large sea freight shipments.
15. What is the difference between personal and commercial import customs clearance?
- Personal import – For private individuals, with simpler customs procedures and possible tax exemptions.
- Commercial import – Requires full customs compliance, reporting, and regulatory approvals.
Businesses must use a customs broker for efficient clearance.