Introduction
In the era of globalization, the world has become a global village where trade between countries, advanced logistics, and international supply chains play a central role in the global economy. From the smartphone in your hand to the food on your table, every product undergoes a complex journey of production, transportation, storage, and distribution before reaching you.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of trade, logistics, and supply chains, with a special focus on the processes of import and export – essential drivers of the modern global economy.
International Trade and the Importance of Import and Export
What are Import and Export?
- Import: The purchase of goods and services from foreign countries for domestic use.
- Export: The sale of goods and services to other countries.
These processes enable countries to leverage their comparative advantages in production and access global markets. For example, a resource-rich country may focus on exporting raw materials, while an industrialized nation specializes in technology products.
Examples:
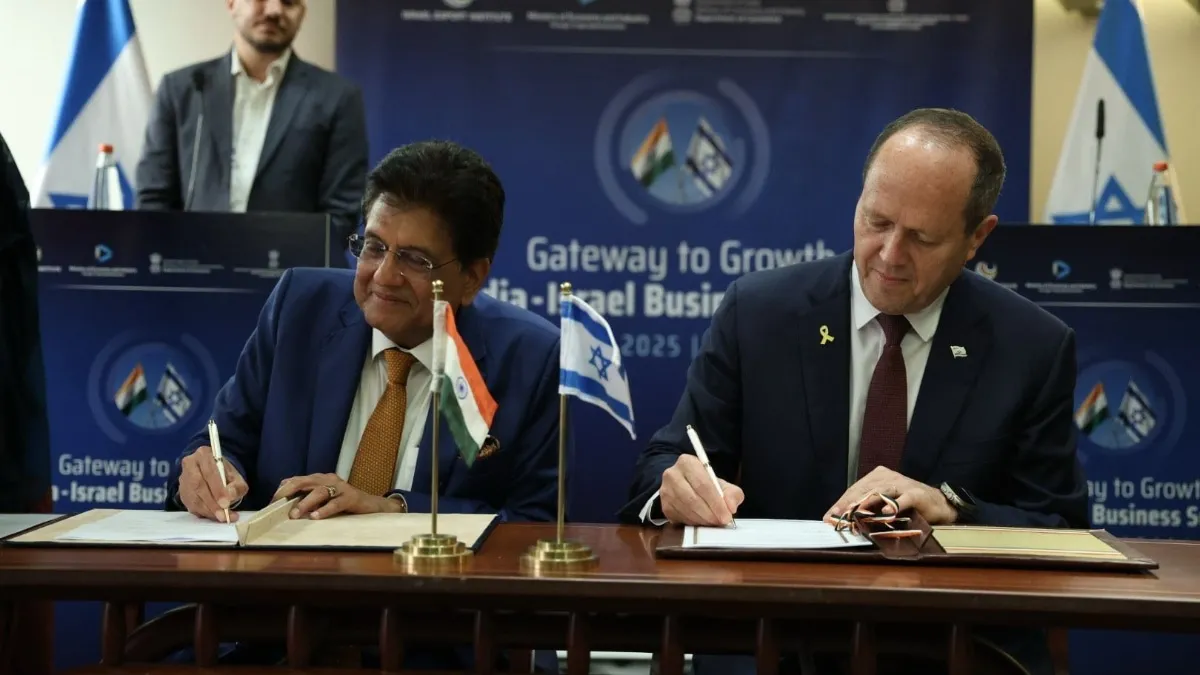
- Import: Cars from Germany, smartphones from China.
- Export: Chemicals, agricultural products, and software from Israel.
Contribution of Import and Export to the Economy
- Increased Variety for Consumers: Consumers gain access to products and services from different countries.
- Boost to National Income: Exports generate revenue and strengthen the balance of payments.
- Innovation and Technology: Imports can introduce new technologies and advanced business models.
Logistics and Supply Chain in Import and Export
The Logistical Challenges in Import and Export
Import and export processes require complex logistical planning, which involves:
- Coordination Between Countries: Compliance with different regulations, taxes, and customs duties.
- Multimodal Operations: Combining sea, air, and land transportation.
- Managing Delivery Times: Ensuring efficiency despite geographical distances.
Supply Chain in Import and Export
An international supply chain involves multiple players – manufacturers, suppliers, distributors, and customs agents – each responsible for a vital part of the process.
Key Steps:
- Sourcing: Identifying suppliers in foreign countries.
- Transportation: Moving goods across countries using a combination of sea, air, and land transport.
- Customs Clearance: A critical process requiring compliance with the import-export laws of the involved countries.
- Local Distribution: Delivering goods to the final destination.
Customs and Regulations in Import and Export
Customs: The Gateway to Global Trade
Customs play a central role in the import and export processes, regulating the movement of goods across borders while collecting taxes and ensuring compliance with local laws.
Challenges in Customs:
- Diverse requirements across countries: Documents, standards, and certifications.
- Delays: Lengthy clearance processes can disrupt supply chains.
- Environmental regulations: New sustainability requirements are becoming more common.
Trade Agreements and Their Impact
Trade agreements between countries, such as NAFTA, the European Union, and free trade agreements with Asian nations, facilitate the movement of goods by reducing tariffs and other barriers. These agreements provide a conducive framework for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to engage in international trade.
Innovative Technologies in Import and Export
- Blockchain: Ensures transparency and accuracy in documentation, such as invoices and customs forms.
- Supply Chain Management Systems: Combining IoT and artificial intelligence to monitor the movement of goods in real-time.
- Robotics and Automation: Enhancing processes in warehouses and border crossings.
Future Trends in Import and Export
1. Shift Toward Sustainability
Many companies are working to reduce the carbon footprint of transportation by integrating renewable energy sources and using electric vehicles.
2. Expansion of E-Commerce
Platforms like Amazon and Alibaba are increasing the volume of international trade, enabling SMEs to offer their products worldwide.
3. Growth in Regional Trade
Alongside globalization, there is a rising emphasis on regional trade due to new trade agreements and shorter delivery times.
Conclusion
Import and export are inseparable from the world of trade, logistics, and supply chain, continuing to serve as a major driver of global economic growth. Proper management of import-export processes requires precise logistical planning, a deep understanding of regulations, and adaptability to changes in the global market.
As technology advances and sustainability takes center stage, import and export processes continue to evolve, offering new opportunities for businesses and consumers worldwide. The integration of innovation, sustainability, and international collaboration promises an exciting future for this field.